From spin-out to scale-up: OpenLight’s $34M funding

Part 1: Start-up funding
OpenLight Photonics, a Santa Barbara-based start-up specialising in silicon photonics, has raised $34 million in an oversubscribed Series A funding round.
The start-up will use the funding to expand production and its photonic integrated circuit (PIC) design staff.
OpenLight Photonics raises $34M in an oversubscribed Series A.
“We’re starting to get customers taking in production mask sets, so it’s about scaling operations and how we handle production,” says OpenLight CEO, Adam Carter (pictured). The start-up needs more PIC designers to work with customers.
Technology
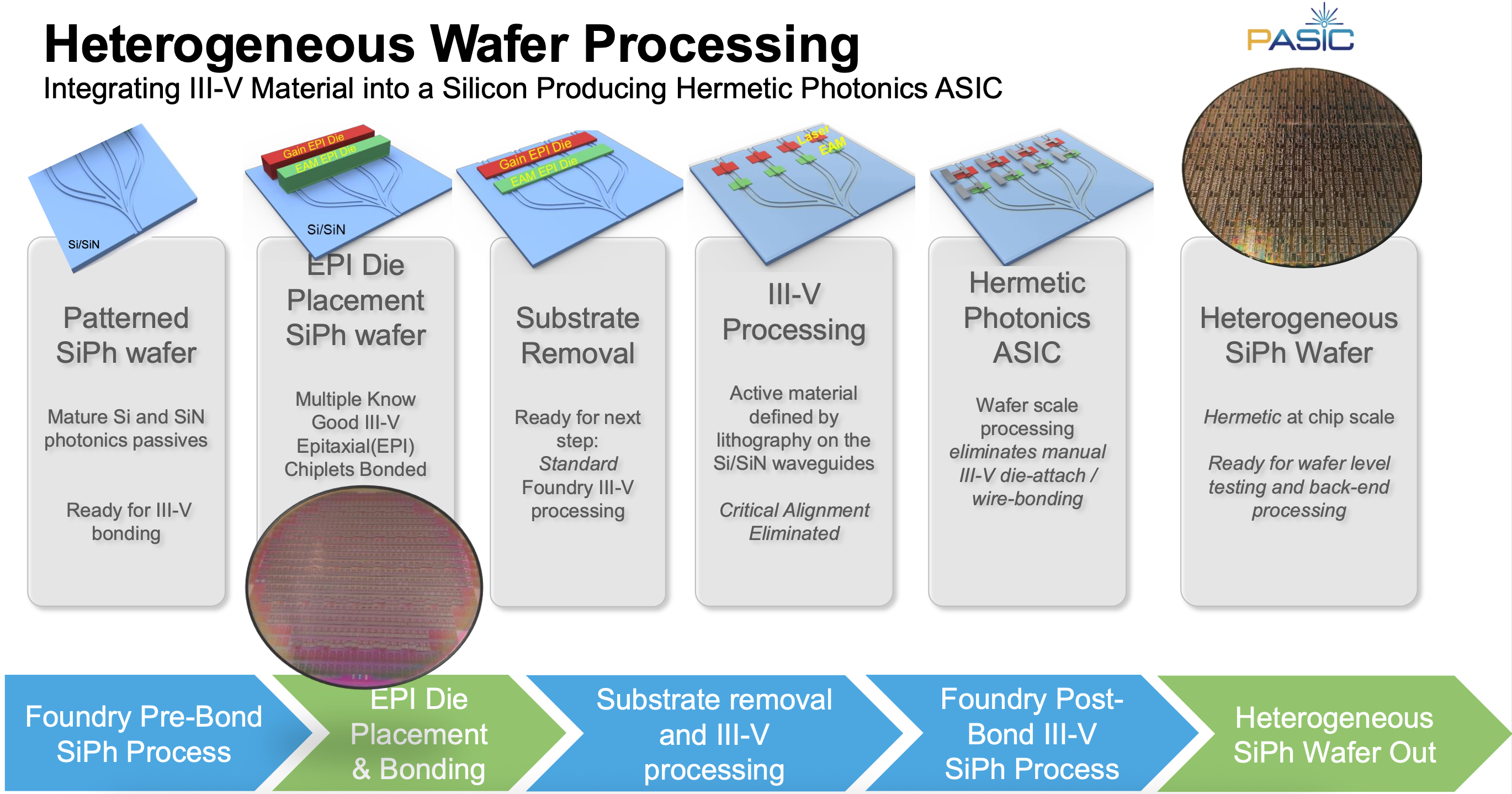
OpenLight’s technology originated at Aurrion, a fabless silicon photonics start-up from the University of California, Santa Barbara.
Aurrion’s heterogeneous integration silicon photonics technology supports III-V materials, enabling components such as lasers, modulators, and optical amplification to be part of a photonic integrated circuit (PIC). Intel has its own heterogeneous integration silicon photonics process, which it has used to make millions of pluggable optical transceivers. OpenLight is offering the technology to customers effectively as a photonic ASIC design house.
Juniper Networks bought Aurrion in 2016 and, in 2022, spun out the unit that became OpenLight. Electronic design tool specialist Synopsys joined Juniper in backing the venture. Synopsys announced it was acquiring simulation company Ansys, a $35 billion deal it completed in July. Given that Synopsys would be focused on integrating Ansys, it suggested to OpenLight in January that they should part ways.
Funding
“We were only looking for $25 million to start with, and we finished at $34 million,” says Carter. Capricorn Investment Group was a late entrant and wanted to co-lead the funding round. Given initial commitments from other funders, Mayfield and Xora Innovation, set specific ownership percentages, it required an increase to accommodate Capricorn.
Xora’s first contact with OpenLight was after it approached the start-up’s stand at the OFC 2025 event held in March.
Juniper—now under HPE—is also an investor. The company played a key role in helping OpenLight while it sought funding. “Juniper could see that we were very close to an intercept point regarding our business model and our customers, so that’s why Juniper invested,” says Carter.
HPE continually looks at technologies it will require; silicon photonics with heterogeneous integration is one such technology, says Carter. However, HPE has no deal with OpenLight at this time.
Design roadmap
OpenLight is developing a 1.6-terabit PIC, now at an advanced prototype (beta) stage. The design uses eight channels for a 1.6T-DR8 OSFP pluggable design, implemented using four lasers and eight modulators, each operating at 200 gigabit-per-second (Gbps).
Carter says the first wafers will come from foundry Tower Semiconductor around October. This will be OpenLight’s largest production run — 100 wafers in four batches of 25. Some ten customers will evaluate the PICs, potentially leading to qualification.
A coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) 1.6-terabit design will follow in 2026. The CWDM uses 4 wavelengths, each at 200Gbps, on a fibre, with two such paths used for the 1.6T OSFP-XD 2xFR4 optical module.
The company is also pushing to develop 400Gbps channels, increasing the frequency response and improving the extinction ratio through process changes.
“We’ve got a whole series of experiments coming out over the next few months,“ says Carter. The frequency response of the indium phosphide modulator has already been improved by 10 gigahertz (GHz) to 90-95GHz. The process changes will be adopted for some alpha sample wafers in production that may enable modulation at 400Gbps, hence a 3.2-terabit PIC design.
“If we can show some good 3.2-terabit eyes, just as a demo, it shows that there’s a technology route to get there whenever 3.2-terabit modules are needed,” he says.
Customer growth
OpenLight’s customers have grown from three in 2023 to 17 last year to 20 actively designing. “We are growing the pipeline,” says Carter.
Early adopters were start-ups, but now larger firms are engaging Openlight. “Investors noted start-ups take more risk, but now bigger companies are coming in to drive volume,” says Carter.
Optical interconnect will drive initial volumes, but automotive and industrial sensing will follow. “The mix will change, but for the next couple of years, the revenues will be from optical interconnect,” says Carter.
Co-packaged optics is another interconnect opportunity. Here, OpenLight’s integrated laser technology would not be needed, given the co-packaged optics designs favour external laser sources. Instead, the company can offer integrated indium phosphide modulator banks or modulator banks with semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs), their compact size—“microns, not millimetres”—aiding packaging.
In addition to the foundry Tower Semiconductor for its wafers, OpenLight partners with Jabil, Sanmina, and TFC for the packaging and does its testing via ISC, an ASE subsidiary.
“They know test and certain customers with ISC, and ASE could do a complete turnkey solution,” says Carter. “But our priority is to get the test area set up to deal with the production; we’ve not had 100 wafers in a year being delivered for test.”
Silicon photonics
Carter, who was at Cisco when it acquired Lightwire in 2012, says silicon photonics’ potential to shrink optical designs was already recognised then. Since then, a lot of progress has been made, but now the focus is on building the supporting ecosystem. This includes a choice of foundries offering optical process design kits (PDKs) and outsourced assembly and test houses (OSATs) that can handle volumes.
Until now, silicon photonics has been all passive circuits. Now OpenLight, working with Tower and its PDK, is offering customers the ability to design and make heterogeneous integrated silicon photonics circuits. “Every customer gets the same PDK,” says Carter.
And it need not just be indium phosphide. The idea is to expand the PDK to support modulation materials such as polymer and thin-film lithium niobate. “If it is a better material, we’ll integrate it,” he says.
Having secured the funding, Carter is clear about the company’s priority: “It’s all about execution now.”
OpenLight's CEO on its silicon photonics strategy

Adam Carter, recently appointed the CEO of OpenLight, discusses the company’s strategy and the market opportunities for silicon photonics.
Adam Carter’s path to becoming OpenLight’s first CEO is a circuitous one.
OpenLight, a start-up, offers the marketplace an open silicon photonics platform with integrated lasers and gain blocks.
Having worked at Cisco and Oclaro, which was acquired by Lumentum in 2018, Carter decided to take six months off. Covid then hit, prolonging his time out.
Carter returned as a consultant working with firms, including a venture capitalist (VC). The VC alerted him about OpenLight’s search for a CEO.
Carter’s interest in OpenLight was immediate. He already knew the technology and OpenLight’s engineering team and recognised the platform’s market potential.
“If it works in the way I think it can work, it [the platform] could be very interesting for many companies who don’t have access to the [silicon photonics] technology,” says Carter.
Offerings and strategy
OpenLight’s silicon photonics technology originated at Aurrion, a fabless silicon photonics start-up from the University of California, Santa Barbara.
Aurrion’s heterogeneous integration silicon photonics technology included III-V materials, enabling lasers to be part of the photonic integrated circuit (PIC).
Juniper Networks bought Aurrion in 2016 and, in 2022, spun out the unit that became OpenLight, with Synopsys joining Juniper in backing the start-up.
OpenLight offers companies two services.
The first is design services for firms with no silicon photonics design expertise. OpenLight will develop a silicon photonics chip to meet the company’s specifications and take the design to production.
“If you don’t have a silicon photonics design team, we will do reference architectures for you,” says Carter.
The design is passed to Tower Semiconductor, a silicon photonics foundry that OpenLight, and before that, Juniper, worked with. Chip prototype runs are wafer-level tested and passed to the customer.
OpenLight gives the company the Graphic Data Stream (GDS) file, which defines the mask set the company orders from Tower for the PIC’s production.
OpenLight also serves companies with in-house silicon photonics expertise that until now have not had access to a silicon photonics process with active components: lasers, semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs), and modulators.
The components are part of the process design kit (PDK), the set of files that models a foundry’s fabrication process. A company can choose a PDK that best suits its silicon photonics design for the foundry to then make the device.
OpenLight offers two PDKs via Tower Semiconductor: a Synopsys PDK and one from Luceda Photonics.
OpenLight does not make components, but offers reference designs. OpenLight gets a small royalty with every wafer shipped when a company’s design goes to production.
“They [Tower] handle the purchasing orders, the shipments, and if required, they’ll send it to the test house to produce known good die on each wafer,” says Carter
OpenLight plans to expand the foundries it works with. “You have to give customers the maximum choice,” says Carter.
Design focus
OpenLight’s design team continues to add components to its library.
At the OFC show in March, held in San Diego, OpenLight announced a 224-gigabit indium phosphide optical modulator to enable 200-gigabit optical lanes. OpenLight also demoed an eight-by-100-gigabit transmitter alongside Synopsys’s 112-gigabit serialiser-deserialiser (serdes).
OpenLight also offers a ‘PDK sampler’ for firms to gain confidence in its process and designs.
The sampler comes with two PICs. One PIC has every component offered in OpenLight’s PDK so a customer can probe and compare test results with the simulation models of Tower’s PDKs.
”You can get confidence that the process and the design are stable,” says Carter.
The second PIC is the eight by 100 gigabit DR8 design demoed at OFC.
The company is also working on different laser structures to improve the picojoule-per-bit performance of its existing design.
“Three picojoules per bit will be the benchmark, and it will go lower as we understand more about reducing these numbers through design and process,” says Carter.
The company wants to offer the most updated components via its PDK, says Carter.
OpenLight’s small design team can’t do everything at once, he says: “And if I have to license other people’s designs into my PDK, I will, to make sure my customer has a maximum choice.”
Market opportunities
OpenLight’s primary market focus is communications, an established and significant market that will continue to grow in the coming years.
To that can be added artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, memory, and high-speed computing, says Carter.
“If you listen to companies like Google, Meta, and Amazon, what they’re saying is that most of their investment in hardware is going into what is needed to support AI and machine learning,” says Carter. “There is a race going on right now.”
When AI and machine learning take off, the volumes of optical connections will grow considerably since the interfaces will not just be for networking but also computing, storage, and memory.
“The industry is not quite ready yet to do that ramp at the bandwidths and the densities needed,” he says, but this will be needed in three to four years.
Large contract manufacturers also see volumes coming and are looking at how to offer optical subassembly, he says.
Another market opportunity is telecoms and, in particular coherent optics for metro networks. However, unit volumes will be critical. “Because I am in a foundry, at scale, I have to fill it with wafers,” says Carter.
Simpler coherent designs – ‘coherent lite’ – connecting data centre buildings could be helpful. There is much interest in short-reach connections, for 10km distances, at 1.6 terabit or higher capacity where coherent could be important and deliver large volumes, he says.
Emerging markets for OpenLight’s platform include lidar, where OpenLight is seeing interest, high-performance computing, and healthcare.
“Lidar is different as it is not standardised,” he says. It is a lucrative market, given how the industry has been funded.
OpenLight wants to offer lidar companies early access to components that they need. Many of these companies have silicon photonics design teams but may not have the actives needed for next-generation products, he says.
“I have a thesis that says everywhere a long-wavelength single-mode laser goes is potential for a PIC,” says Carter
Healthcare opportunities include a monitoring PIC placed on a person’s wrist. Carter also cites machine vision, and cell phone makers who want improved camera depth perception in handsets.
Carter is excited by these emerging silicon photonics markets that promise new incremental revenue streams. But timing will be key.
“We have to get into the right market at the right time with the right product,” says Carter. “If we can do that, then there are opportunities to grow and not rely on one market segment.”
As CEO, how does he view success at OpenLight?
“The employees here, some of whom have been here since the start of Aurrion, have never experienced commercial success,” says Carter. “If that happens, and I think it will because that is why I joined, that would be something I could be proud of.”